23.05.19
World Day Against Child Labour 12 June.
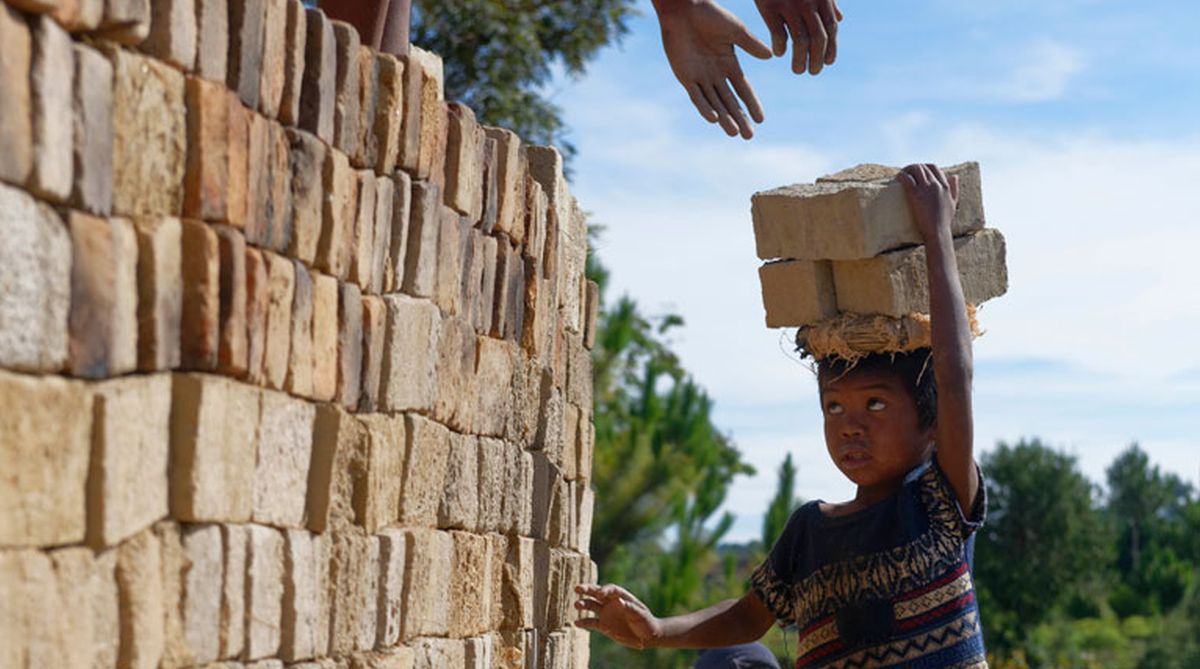
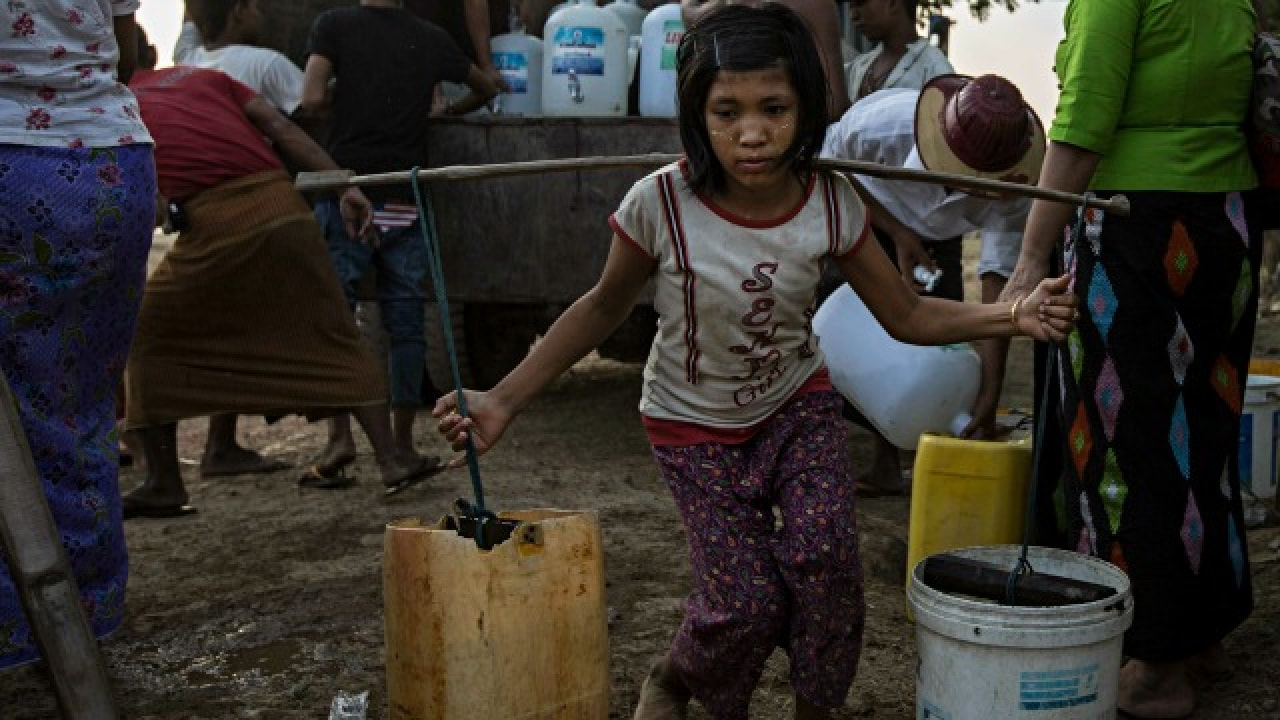
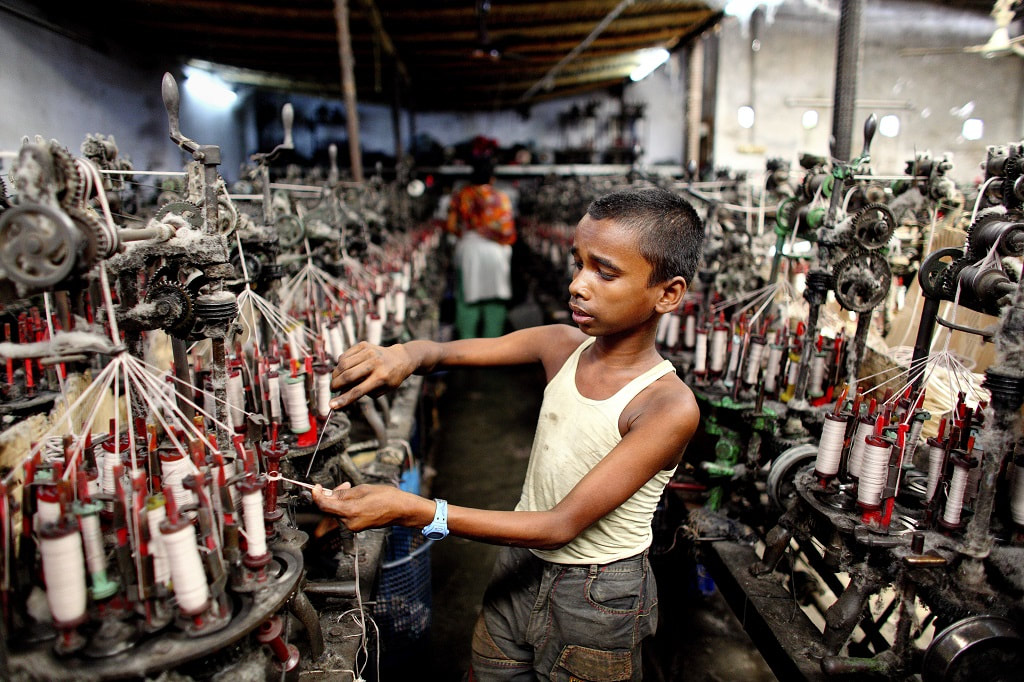
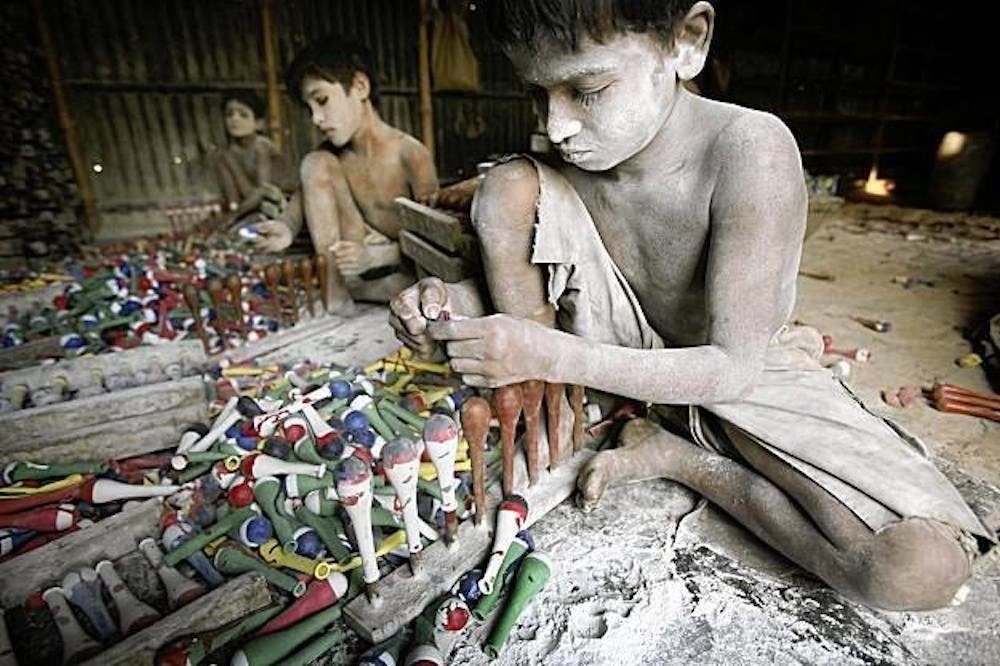
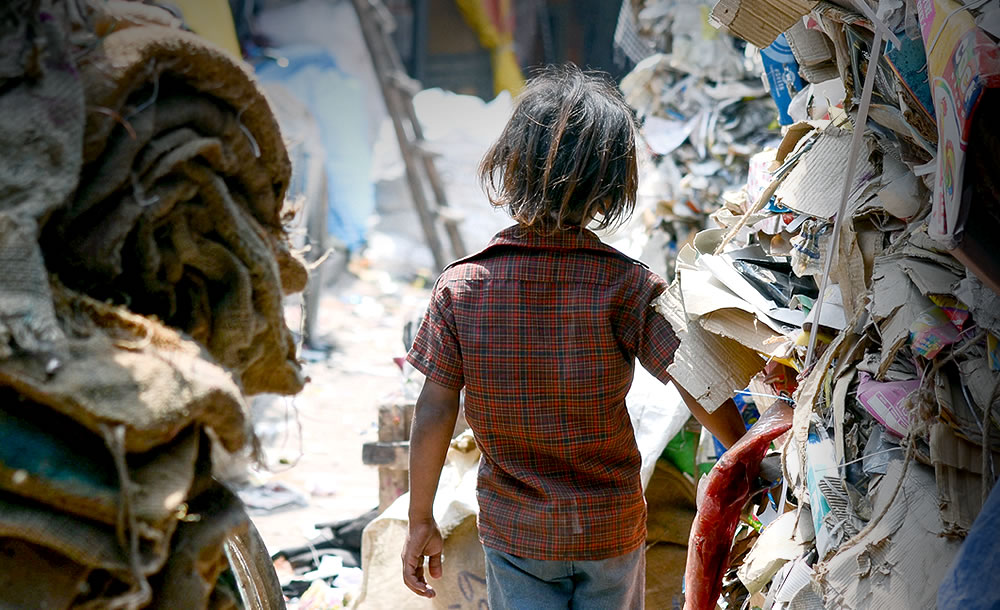
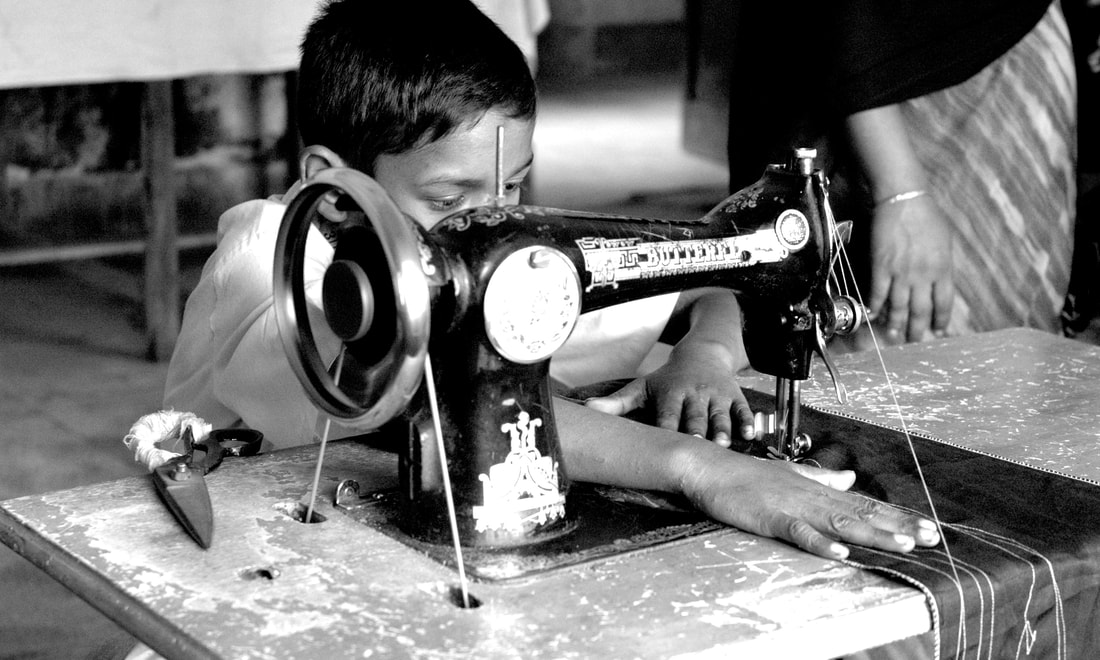
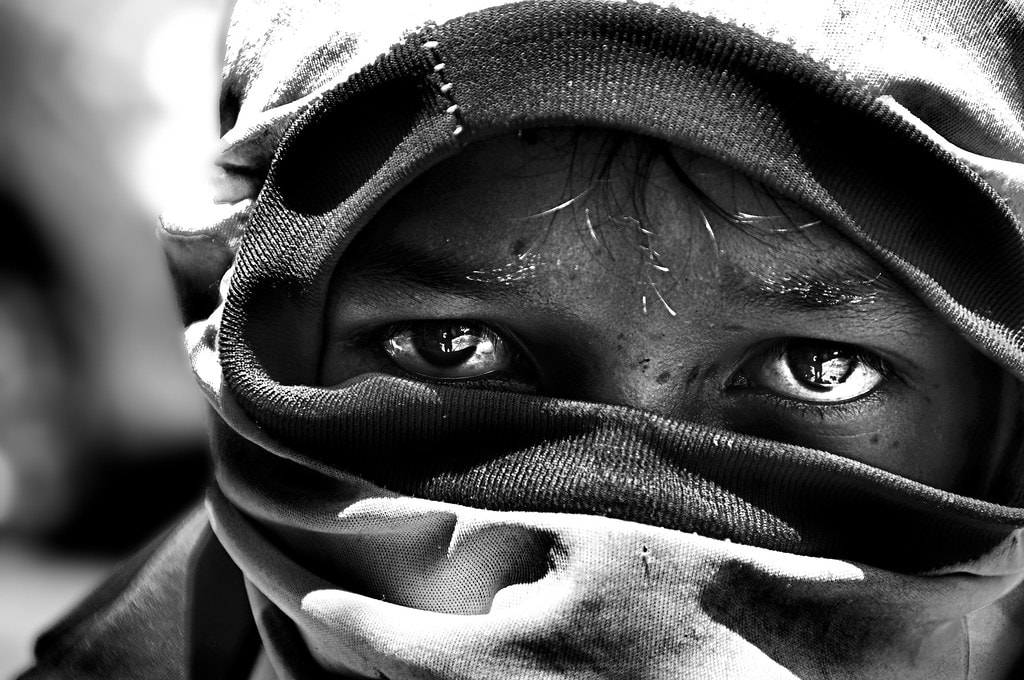
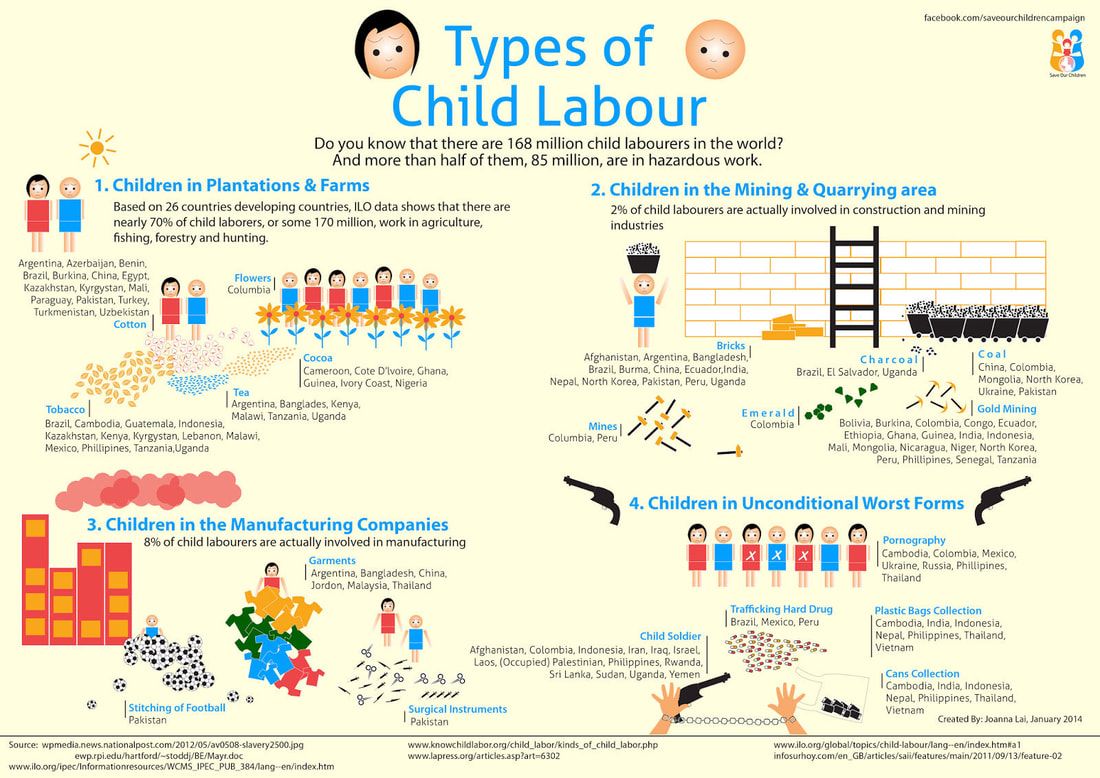
Today, throughout the world, around 218 million children work, many full-time. They do not go to school and have little or no time to play. Many do not receive proper nutrition or care. They are denied the chance to be children. More than half of them are exposed to the worst forms of child labour such as work in hazardous environments, slavery, or other forms of forced labour, illicit activities including drug trafficking and prostitution, as well as involvement in armed conflict.
What is meant by child labour ?
Child labour is work carried out to the detriment and endangerment of a child, in violation of international law and national legislation. It either deprives children of schooling or requires them to assume the dual burden of schooling and work. Child labour to be eliminated is a subset of children in employment. It includes:
What is meant by child labour ?
Child labour is work carried out to the detriment and endangerment of a child, in violation of international law and national legislation. It either deprives children of schooling or requires them to assume the dual burden of schooling and work. Child labour to be eliminated is a subset of children in employment. It includes:
- All “unconditional” worst forms of child labour, such as slavery or practices similar to slavery, the use of a child for prostitution or for illicit activities;
- Work done by children under the minimum legal age for that type of work, as defined by national legislation in accordance with international standards.
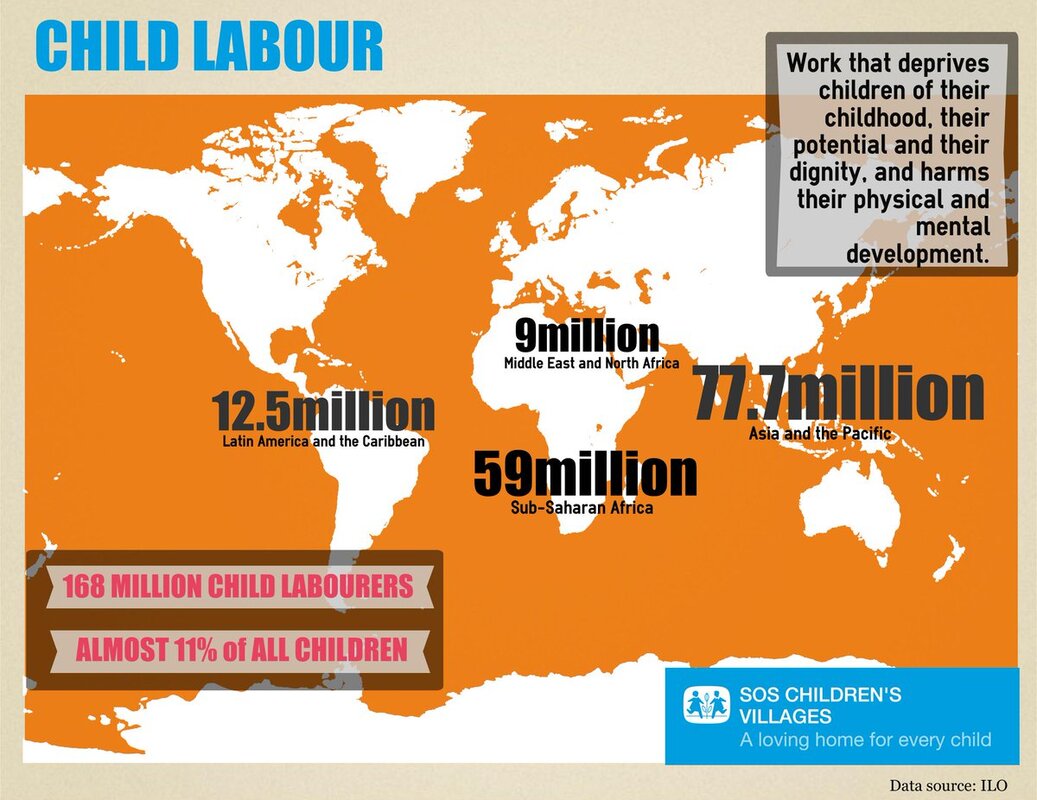
- Worldwide 218 million children between 5 and 17 years are in employment.
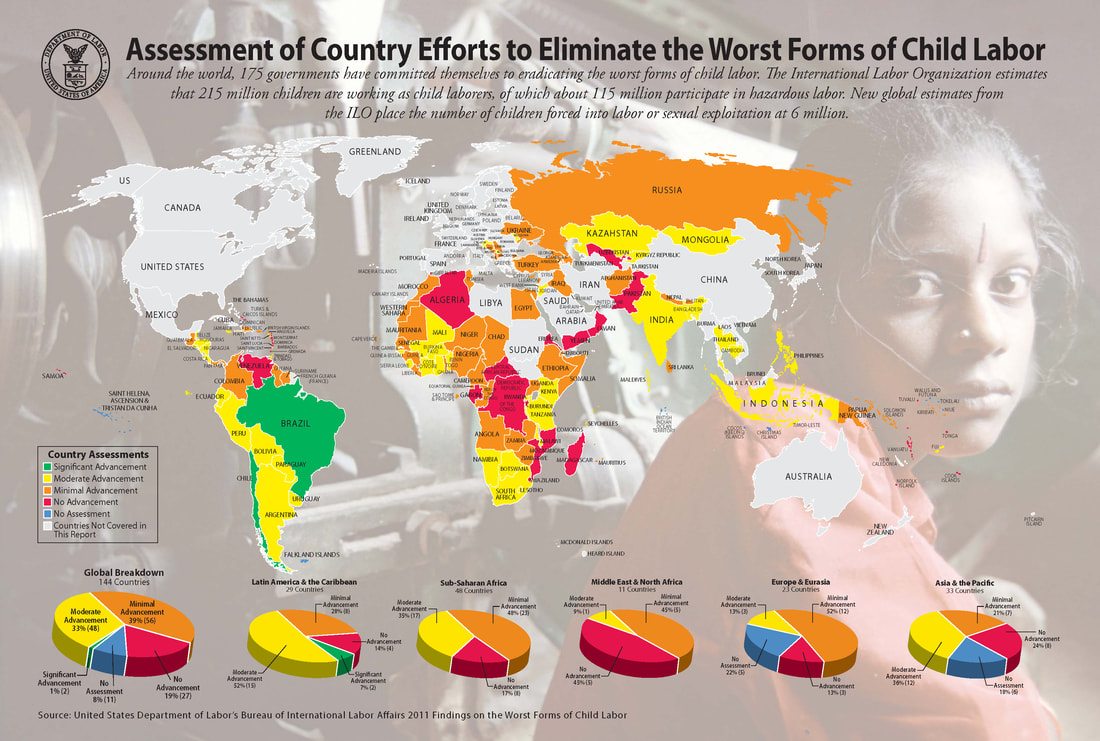
Among them, 152 million are victims of child labour; almost half of them, 73 million, work in hazardous child labour. - In absolute terms, almost half of child labour (72.1 million) is to be found in Africa; 62.1 million in the Asia and the Pacific; 10.7 million in the Americas; 1.2 million in the Arab States and 5.5 million in Europe and Central Asia.
- In terms of prevalence, 1 in 5 children in Africa (19.6%) are in child labour, whilst prevalence in other regions is between 3% and 7%: 2.9% in the Arab States (1 in 35 children); 4.1% in Europe and Central Asia (1 in 25); 5.3% in the Americas (1 in 19) and 7.4% in Asia and the Pacific region (1 in 14).
- Almost half of all 152 million children victims of child labour are aged 5-11 years.
42 million (28%) are 12-14 years old; and 37 million (24%) are 15-17 years old. - Hazardous child labour is most prevalent among the 15-17 years old. Nevertheless up to a fourth of all hazardous child labour (19 million) is done by children less than 12 years old.
- Among 152 million children in child labour, 88 million are boys and 64 million are girls.
- 58% of all children in child labour and 62% of all children in hazardous work are boys. Boys appear to face a greater risk of child labour than girls, but this may also be a reflection of an under-reporting of girls’ work, particularly in domestic child labour.
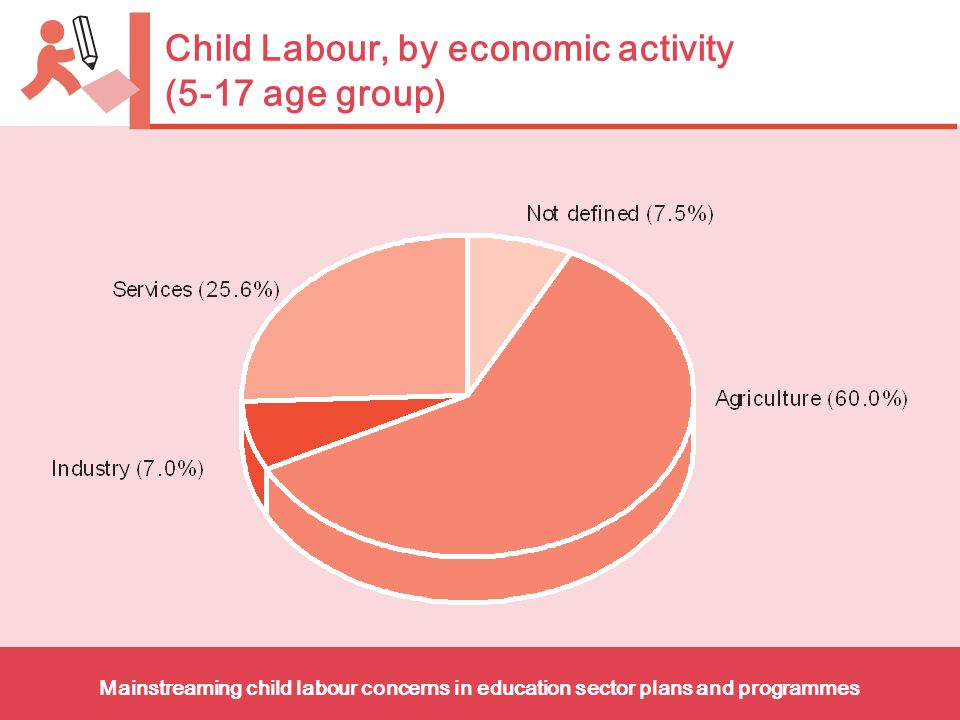
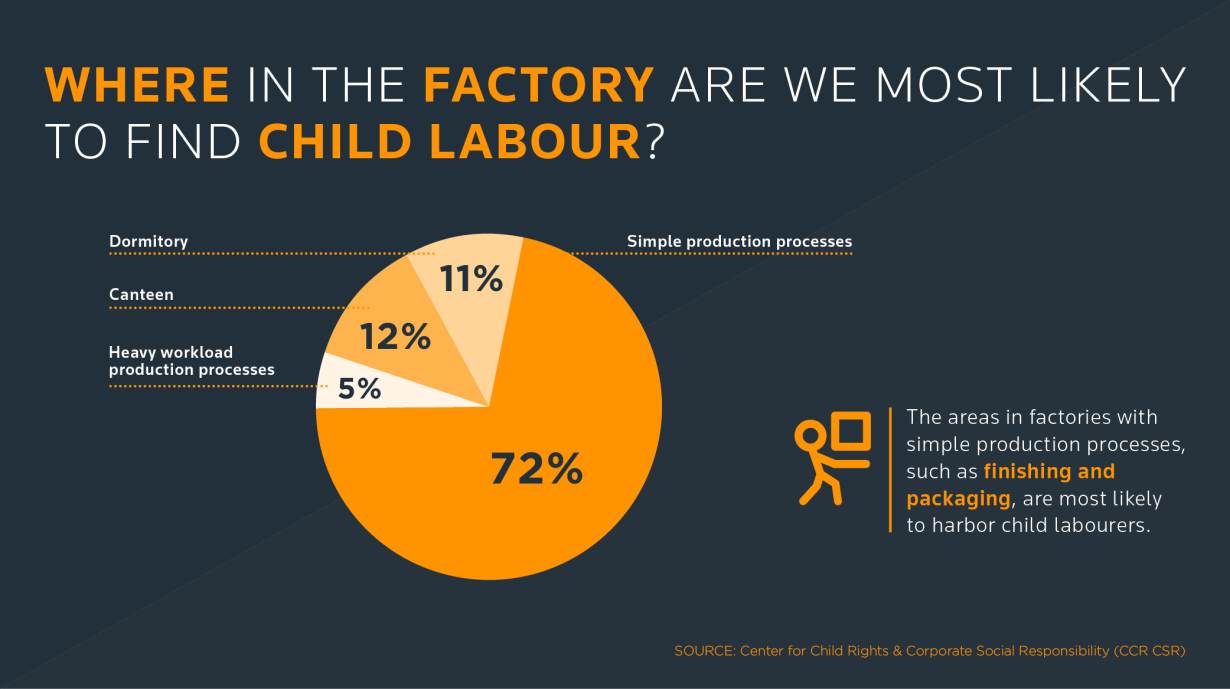
- Child labour is concentrated primarily in agriculture (71%), which includes fishing, forestry, livestock herding and aquaculture, and comprises both subsistence and commercial farming; 17% in Services; and 12% in the Industrial sector, including mining.
Poverty deprives people of adequate education, health care and of life's most basic necessities- safe living conditions (including clean air and clean drinking water) and an adequate food supply. The developed (industrialized) countries today account for roughly 20 percent of the world's population but control about 80 percent of the world's wealth.
Poverty and pollution seem to operate in a vicious cycle that, so far, has been hard to break. Even in the developed nations, the gap between the rich and the poor is evident in their respective social and environmental conditions.
Poverty and pollution seem to operate in a vicious cycle that, so far, has been hard to break. Even in the developed nations, the gap between the rich and the poor is evident in their respective social and environmental conditions.